What is Carrier Screening?
Carrier screening is a genetic test used to evaluate if a person is a carrier of a genetic condition. Focusing primarily on early onset, severe disorders that follow either autosomal recessive or X-linked recessive modes of inheritance, carrier screening aims to detect couples who are at risk of passing down these genetic conditions to their children.
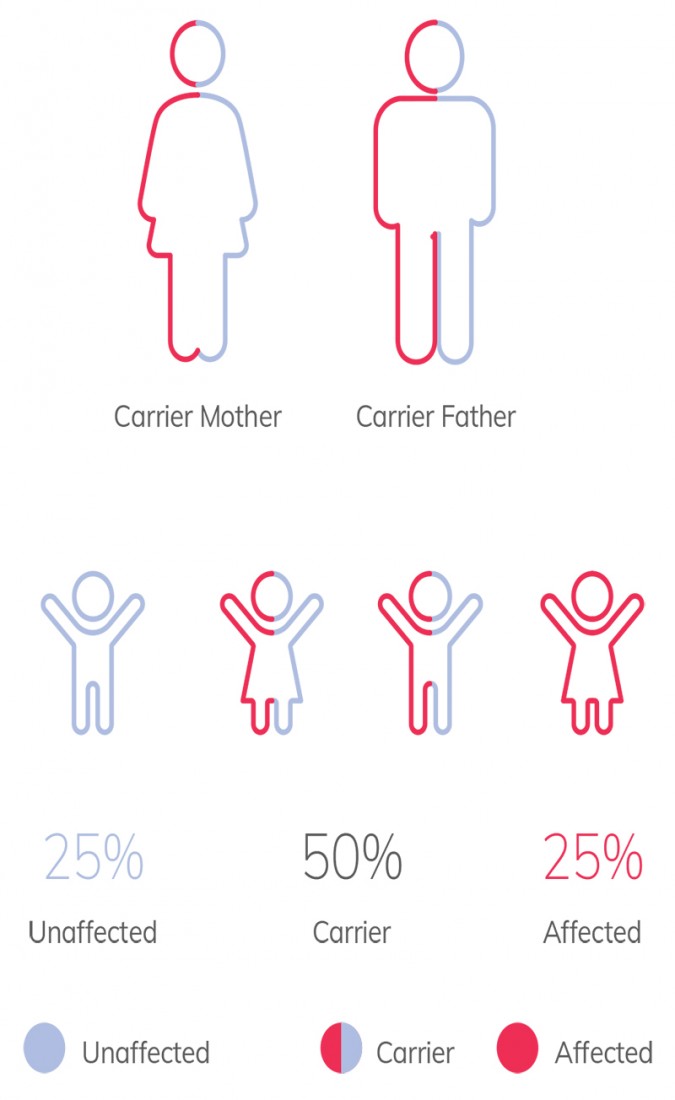
Autosomal Recessive Genetic Conditions
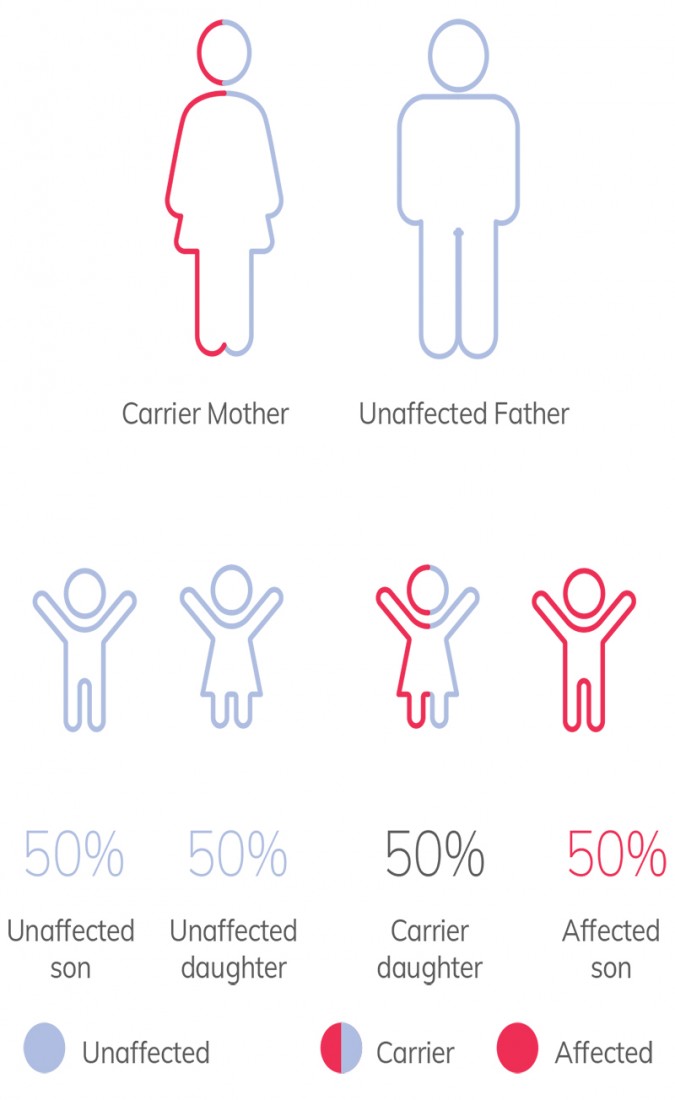
X-linked Recessive Genetic Conditions
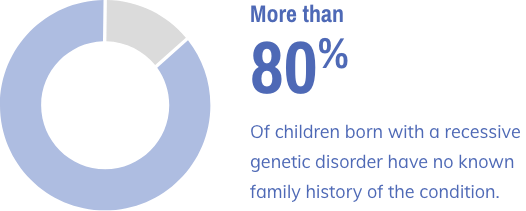
PsiGenex's Approach:
At PsiGenex we are revolutionizing reproductive health and transforming the approach to carrier screening.
Carrier Screening Today
Carrier screening was traditionally targeted testing for specific genetic disorders, based on an individual’s ethnicity or family history. However, this limited approach may fail to identify couples at risk of passing down genetic disorders. A more suitable approach for today’s society is comprehensive screening which adopts a more wide-ranging strategy by including more genes and variants, regardless of family history or ethnicity.
Comprehensive Screening
- Screens for hundreds of disorders simultaneously
- Offered to everyone regardless of family history or ethnicity
- Self-reporting is not required, eliminating incorrect panel selection
- Increases carrier detection rates to capture the highest amount of at-risk individuals
Targeted Screening
- Selective testing for a small group of disorders
- Offered based on family history or ethnicity
- Self-reported information is required
- Limited so can miss up to 70% of carriers
Advantages of Early Screening
Carrier Screening Panels at PsiGenex
Comprehensive Carrier Screening Panel
Screens for all 431 pertinent genetic disorders that cause a wide range of severe medical and intellectual symptoms. Panel covers common mutations in 421 genes, as well as those that are more rare, making it the screening option that gives patients the most comprehensive risk assessment.
Ashkenazi Jewish Carrier Screening Panel
Screens for 61 genetic disorders that are most prevalent in people of Ashkenazi Jewish descent. Includes Tay-Sachs disease, Canavan disease, Cystic Fibrosis, Spinal Muscular Atrophy, and Fragile X syndrome.
ACOG/ACMG Carrier Screening Panel
Screens for 15 common disorders that are recommended to women by the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACOG) and the American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACMG). Includes Cystic Fibrosis, Spinal Muscular Atrophy, and Fragile X syndrome.
Core Carrier Screening Panel
Screens for three common genetic disorders:
- Cystic Fibrosis - the most common autosomal recessive disorder
- Spinal Muscular Atrophy - second most common, lethal, autosomal recessive disorder
- Fragile X Syndrome - X-linked disorder, leading cause of intellectual disabilities

.png)